1409-K: Difference between revisions
(→Photos) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{GR Product | |||
|model=1409-K | |||
|codes=1409-1409-9711 | |||
|class=Capacitance Standards | |||
|summary=0.005μF,0.05% Standard Capacitor | |||
|image=GR 1409-K Close-Up.jpg | |||
|caption=General Radio 1409-K Standard Capacitor | |||
|series=1409 | |||
|introduced=1956 | |||
|discontinued=1970 | |||
|designers= | |||
|manuals= | |||
* '''Manual Needed.''' | |||
{{Catalog History}} | |||
}} | |||
The {{Title|General Radio General Radio 1409-K Standard Capacitor}} was introduced in {{Catalog O}} and remained available through {{Catalog U}}. | |||
The 1409-K is a fixed mica capacitor of very high stability for use as two or three-terminal capacitance standards in the laboratory. The capacitor is installed in an aluminum case along with Silica gel desiccant then sealed with hi-temp potting wax. A well located on the right side of the case for the insertion of a dial-type thermometer. Three jack-top binding posts are provided on the top of the case and removable plugs on the bottom, for convenient parallel connection without error. Each capacitor is supplied with a certificate of calibration giving two and three terminal measured capacitance. | |||
See [[1409]] to view all the capacitors in the series. | |||
==Specifications== | ==Specifications== | ||
* '''Capacitance:''' 0.005 μF | |||
* '''Series Inductance:''' 0.050 μH | |||
* '''Adjustment Accuracy:''' within ±0.05% | |||
* '''Stability:''' Capacitance change is less than 0.01% per year | |||
* '''Temperature Coefficient: capacitance; +35 ± 10 ppm per degree between 10 °C and 70 °C | |||
* '''Dissipation Factor: Less than 0.0003 at 1 kHz and 23 °C (see curves). Measured dissipation factor at 1 kHz is stated in the | |||
certificate to an accuracy of ±0.00005 | |||
* '''Leakage Resistance:''' 5000 ohm-farads or 100 GΩ, whichever is the lesser | |||
* '''Maximum Voltage:''' 500 V peak below 1.3 MHz | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
* [[Media:GR Exp 1409 07_1957.pdf|Experimenter July 1957 describing Type 1409 Series]] | |||
==Photos== | ==Photos== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
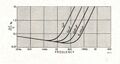
GR 1209 Figure 1.jpg|Change in capacitance as a function of frequency for typical Type 1409 capacitors. | |||
GR 1209 Figure 2.jpg|Dissipation factor as a function of frequency. | |||
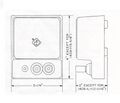
GR 1409 Technical Drawing.jpg|Technical Drawing. | |||
GR 1409-K Close-Up.jpg | GR 1409-K Close-Up.jpg | ||
GR 1409 Small Case Left.jpg| Thermometer Access | GR 1409 Small Case Left.jpg| Thermometer Access | ||
Revision as of 03:32, 21 June 2024
The General Radio General Radio 1409-K Standard Capacitor was introduced in Catalog O (1956) and remained available through Catalog U (1970).
The 1409-K is a fixed mica capacitor of very high stability for use as two or three-terminal capacitance standards in the laboratory. The capacitor is installed in an aluminum case along with Silica gel desiccant then sealed with hi-temp potting wax. A well located on the right side of the case for the insertion of a dial-type thermometer. Three jack-top binding posts are provided on the top of the case and removable plugs on the bottom, for convenient parallel connection without error. Each capacitor is supplied with a certificate of calibration giving two and three terminal measured capacitance.
See 1409 to view all the capacitors in the series.
Specifications
- Capacitance: 0.005 μF
- Series Inductance: 0.050 μH
- Adjustment Accuracy: within ±0.05%
- Stability: Capacitance change is less than 0.01% per year
- Temperature Coefficient: capacitance; +35 ± 10 ppm per degree between 10 °C and 70 °C
- Dissipation Factor: Less than 0.0003 at 1 kHz and 23 °C (see curves). Measured dissipation factor at 1 kHz is stated in the
certificate to an accuracy of ±0.00005
- Leakage Resistance: 5000 ohm-farads or 100 GΩ, whichever is the lesser
- Maximum Voltage: 500 V peak below 1.3 MHz
Links
Photos
-
Change in capacitance as a function of frequency for typical Type 1409 capacitors.
-
Dissipation factor as a function of frequency.
-
Technical Drawing.
-
-
Thermometer Access
-
-
-
-